Employee Salary Slip: A Complete Details
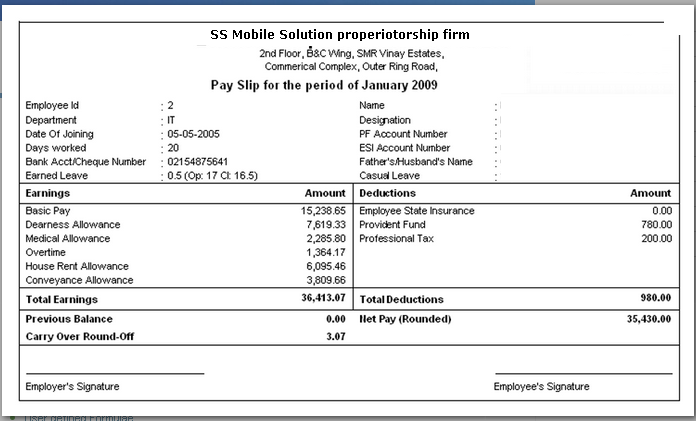
An employee salary slip is one of the most important financial documents for any working professional. It acts as proof of employment, income, and tax deductions. Every month, employees receive a salary slip from their employer, which provides a complete breakdown of earnings and deductions. Understanding this document is crucial for financial planning, loan applications, and income tax filing.
What is an Employee Salary Slip?
An employee salary slip is a monthly statement issued by the employer that contains detailed information about the employee’s gross salary, various allowances, deductions, and net pay. It serves as an official record of how much the employee earned during a particular month and how much was deducted for statutory or voluntary purposes.
This document is not only proof of payment but also acts as a reference for various purposes such as applying for credit cards, home loans, personal loans, and even for visa applications. Employers usually provide salary slips in a printed or digital format.
Key Components of an Employee Salary Slip
A typical salary slip has two major sections – earnings and deductions. Understanding these sections helps employees know their exact take-home salary.
1. Earnings Section
This section includes all the components that add to the employee’s gross salary.
- Basic Salary – This is the fixed component of the salary and forms a major part of the total earnings. It is fully taxable.
- Dearness Allowance (DA) – Mainly provided in government jobs and some private organizations to adjust for inflation.
- House Rent Allowance (HRA) – Given to employees to meet their rental expenses. It can provide tax benefits under certain conditions.
- Conveyance or Transport Allowance – Paid to cover daily travel expenses from home to office.
- Medical Allowance – A fixed allowance for medical expenses.
- Special Allowance – Any extra allowance given by the employer apart from the above components.
- Overtime or Incentives – Additional earnings for extra working hours or performance-based incentives.
2. Deductions Section
This section shows the amounts deducted from the gross salary.
- Provident Fund (PF) – A compulsory saving scheme where both employee and employer contribute a fixed percentage of the basic salary.
- Professional Tax (PT) – A small tax levied by state governments on salaried employees.
- Income Tax (TDS) – Tax deducted at source as per the applicable income tax slab.
- Health Insurance or Other Voluntary Deductions – Any premium or voluntary deductions requested by the employee.
After all deductions, the remaining amount is known as net salary or take-home salary.
Why is an Employee Salary Slip Important?
Salary slips are not just proof of payment; they have multiple uses in professional and personal financial matters.
- Proof of Income – A salary slip is required while applying for loans, credit cards, or any financial product.
- Income Tax Filing – It helps in calculating annual income and claiming exemptions or deductions.
- Negotiating Future Salary – When changing jobs, salary slips are often required to negotiate better offers.
- Employment Verification – Employers may ask for previous salary slips to verify your employment history.
- Legal Records – It acts as legal proof in case of any salary-related disputes.
Digital vs Physical Salary Slips
Earlier, most companies provided printed salary slips. However, with technological advancements, digital salary slips have become common. Digital slips are easier to store, access, and share when required. Employees can download them from company portals, making the process more efficient.
How to Read an Employee Salary Slip
Many employees simply check the net salary credited to their account without analyzing the details. However, reading and understanding a salary slip helps identify errors and plan taxes better. Key things to check include:
- Gross salary
- Allowances mentioned
- Deductions for PF, PT, and TDS
- Net salary after all deductions
It is advisable to verify the details every month to ensure accuracy.
Salary Slip Formats
The format of a salary slip may vary from one organization to another, but the core components remain the same. A typical salary slip format includes:
- Employee details like name, ID, designation, and department
- Employer details like company name and logo
- Salary period (month and year)
- Earnings section
- Deductions section
- Gross salary and net salary
- Signature or digital stamp of the employer
Retaining Salary Slips
Employees should keep a record of their salary slips, whether in physical or digital form. Maintaining salary slips for at least a few years is important for tax assessments, future employment verification, and loan processing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many employees ignore salary slips and only focus on the credited amount. This can lead to confusion later, especially during tax filing. Common mistakes include:
- Not verifying the allowances and deductions
- Misunderstanding tax components
- Losing salary slips and facing trouble during financial applications
Always review your salary slip carefully and maintain a secure copy.
Conclusion
An employee salary slip is much more than just a monthly payment record. It provides a transparent view of earnings, deductions, and tax liabilities. Understanding each component of the salary slip empowers employees to plan their finances, save on taxes, and ensure accurate record-keeping. Whether you are a fresher or an experienced professional, always review and preserve your salary slips for future needs.


