Understanding What Is a Flight of Stairs
When designing or exploring buildings, one of the fundamental architectural elements to consider is the staircase. Whether you’re remodeling a home or constructing a new commercial space, understanding the components of stairs is essential. A common term that often arises in this context is what is a flight of stairs. Knowing this concept helps in planning, safety, and compliance with building codes.
What Does a Flight of Stairs Really Mean?
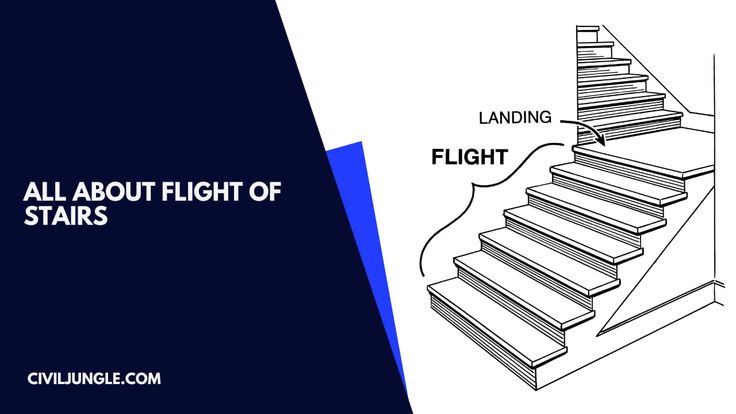
Simply put, a flight of stairs refers to a continuous series of steps between two floors or levels without any intermediate landing or interruption. It represents the main vertical segment connecting one level to another in a building. For example, when you ascend from the ground floor to the first floor without stopping, you’re climbing a flight of stairs.
A typical flight can range from 8 to 16 steps, depending on the height between floors and building codes. In architectural terms, if there’s a landing or platform midway, the staircase is usually divided into two flights. Flights of stairs are commonly found in residential homes, commercial buildings, schools, and public venues, and they can be constructed from various materials such as wood, concrete, metal, or stone.
Flights of stairs also play a crucial role in emergency evacuations, which is why their design, railing height, and step uniformity are often strictly regulated for safety and accessibility. Beyond function, stair flights can also serve as aesthetic elements, influencing a building’s interior design and flow.
Components of a Flight of Stairs
A typical flight of stairs comprises several important parts:
- Treads: The flat surfaces you step on.
- Risers: The vertical components between each tread.
- Stringers: The structural supports on either side of the stairs.
- Landing: A flat platform at the top or bottom of a flight, providing a resting or turning point.
Together, these elements form a complete and functional staircase segment.
Why Understanding What Is a Flight of Stairs Is Important
Knowing what constitutes a flight of stairs helps in multiple ways. It ensures that custom staircase designs adhere to safety standards, such as proper dimensions for treads and risers. It also simplifies the communication with architects and contractors, who need precise terminology to execute projects effectively. Additionally, recognizing what a flight of stairs is becomes vital when inspecting or maintaining existing structures.
Legal and Safety Considerations
Building codes typically specify the maximum height for a single flight of stairs and the number of steps allowed before a landing is required. This is to prevent fatigue and accidents. For example, many codes define that a flight must not exceed 12-14 steps without a landing. Understanding what is a flight of stairs aids in compliance, ensuring safety for all users.
Different Types of Flights of Stairs
Flights can vary in design based on the space constraints and aesthetic preferences. Some common types include straight flights, L-shaped stairs, U-shaped stairs, and spiral stairs. Each type has a specific configuration of flights and landings, but the core concept remains the same: they are all segments of stairs that connect levels.
For a more detailed explanation of this term and related building elements, you can visit the page on what is a flight of stairs.
Conclusion
In summary, a flight of stairs is a crucial component of building design that connects two levels in a continuous and safe manner. Whether you are an architect, builder, or homeowner, understanding this concept helps ensure safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing staircases. When planning your next project, always consider the definition and components of a flight of stairs to meet safety standards and achieve your desired design outcome.
For more information about various building elements and construction tips, visit the homepage.


